Data Types
Python has the following data types built-in by default
Text Type: str
Numeric Types: int, float, complex Sequence Types: list, tuple, range Mapping Type: dict
Set Types: set, frozenset
Boolean Type: bool
Binary Types: bytes, bytearray, memoryview
None Type: NoneType
Variable
Variable is a container that is used to store values of any above mentioned data type. for example:-
name = "Khurram Arshad" x = 12
y = 10.23
z = 2 + 3j
my_list = [ 1, 2, 11, "wNeuron", 3.34, 2-4j ]
my_tuple = ( 1, 2, 11, "wNeuron", 3.34, 2-4j ) my_range = range(1,10)
my_dict = { "name" : "wNeuron", "contact": "03124000464" } my_set = { 1, 2, 11, "wNeuron", 3.34, 2-4j }
my_frozen_set = frozenset({ 1, 2, 11, "wNeuron", 3.34, 2-4j }) is_active = True
is_active = False
arr = bytes(name, 'utf-8') #output will be b'Khurram Arshad' value = None
variable Naming Convention:- Use a lowercase single letter, word, or words. Separate words with underscores to improve readability.also we can not define variable say like as 3a or a-3 or just 3 if
you want to use numbers in variable we can write it as a_3
String Data Type (str)
name = "Geeks for Geeks!"
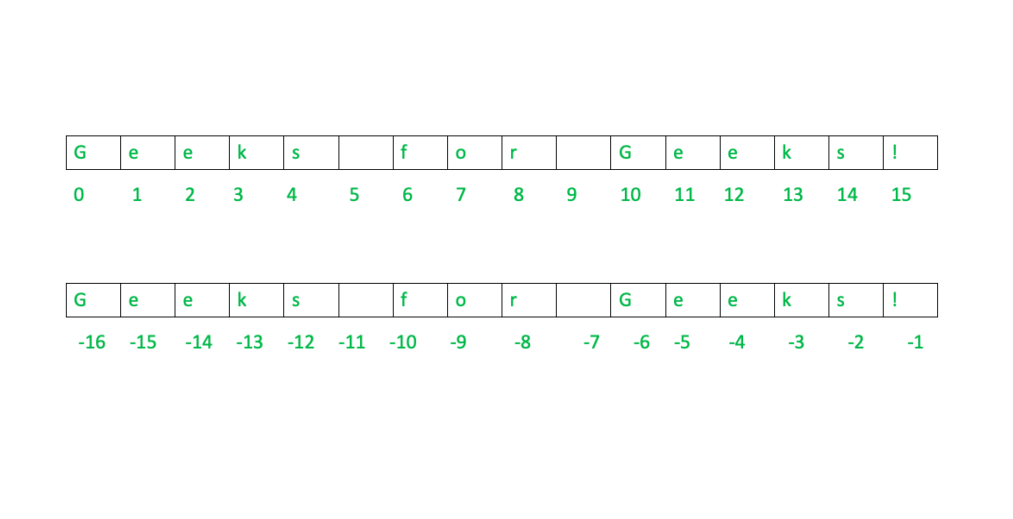
name
'Geeks for Geeks!'
name[0]
'G'
name[6]
'f'
name[-2]
's'
name[0:5]
'Geeks'
name[-10:-2]
'for Geek'
name[0:10:3]
'Gkf '
name[-10:-2:3]
'f e'
syntax:-
var_name[start_index : end_index : step_size]
Sting Methods
sentence = "hello, I Am doing MASTERS in Machine learning from wNeuron."
type(sentence)
str
sentence.capitalize() # Converts the first character to upper case
'Hello, i am doing masters in machine learning from wneuron.'
text = "HELLO, How are YoU"
text.casefold() # Converts string into lower case
'hello, how are you'
txt = "I love apples, apple are my favorite fruit."
txt.count("apple") # Returns the number of times a specified value occurs in a strin 2
my_txt = "Hello, welcome to my world."
txt.endswith(".") # Returns true if the string ends with the specified value True
txt_1 = "Hello, welcome to my world."
txt_1.find("welcome") # Searches the string for a specified value and returns the po 7
price_txt = "For only {price} dollars!"
"For only {num} dollars! {price}".format(price=12 ,num=10)
'For only 10 dollars! 12'
price_txt.format(price = 49) # Formats specified values in a string
'For only 49 dollars!'
price_txt_1 = "For only {price:.2f} dollars!"
price_txt_1.format(price = 49)
'For only 49.00 dollars!'
price_txt_2 = "For only {} dollars!"
price_txt_2.format(49.99)
'For only 49.99 dollars!'
simple_text = "my name is {}, and age is {}"
simple_text.format("Khurram", 70)
'my name is Khurram, and age is 70'
Note: All string methods returns new values. They do not change the original string.
Assignment-1:-
consider the following paragraph given below
my_para = "i started my journy of life in [1980], completed masters in mathematics from [University of Punjab]."
you are supposed to remove all square brackets '[ ]' from the above para.
also stores the new output in a new variable named "my_new_para" and show the outputs of both variables.
# solution
my_para = "i started my journy of life in [1980], completed masters in mathematics f
temp1 = my_para.replace("[","$")
temp1
'i started my journy of life in $1980], completed masters in mathematics f
rom $University of Punjab] '
my_new_para = temp1.replace("]","") my_new_para
'i started my journy of life in 1980, completed masters in mathematics fro
m University of Punjab '
Integer, Float and Complex Data Type
roll_number = 1244
type(roll_number) int
price = 12.33
type(price)
float
z = 2+3j
type(z)
complex
List Data Type
my_list = [ 1, 2, 11, "wNeuron", 3.34, 2-4j ]
type(my_list) list
my_list[0] 1
my_list[-1]
(2-4j)
my_list[0:4]
[1, 2, 11, 'wNeuron']
my_list[-3:-1]
['wNeuron', 3.34]
my_list[0:5:3]
[1, 'wNeuron']
List Methods
color_list = ["red", "green"]
len(color_list) # getting length of a list that how many items a list contains 2
color_list.append("yellow") # append new items into a list
color_list
['red', 'green', 'yellow']
new_color_list = ['blue', 'purple', 'orannge']
color_list.extend(new_color_list) # Add the elements of a list, to the end of the cu
color_list
['red', 'green', 'yellow', 'blue', 'purple', 'orannge']
color_list.insert(1, "wNeuron") # Adds an element at the specified position
color_list
['red', 'wNeuron', 'green', 'yellow', 'blue', 'purple', 'orannge']
color_list.pop(2) # Removes the element at the specified position
'green'
color_list
['red', 'wNeuron', 'yellow', 'blue', 'purple', 'orannge']
color_list.remove("yellow") # Removes the first item with the specified value
color_list
['red', 'wNeuron', 'blue', 'purple', 'orannge']
num_list = [12, 1, 23, 13]
num_list.sort() #Sorts the list
num_list
[1, 12, 13, 23]
num_list.reverse() # Reverses the order of the list
num_list
[23, 13, 12, 1]
Note:-
Lists are mutable
Tuple Data Type
roll_numbers = (1100, 1101, 1102)
type(roll_numbers) tuple
roll_numbers[0]
1100
roll_numbers[2]
1102
tuple Methods
random_numbers = (1, 1, 12, 13, 1, 12)
random_numbers.count(12) # Returns the number of times a specified value occurs in a 2
random_numbers.index(13) #Searches the tuple for a specified value and returns the 3
Note:-
tuples are immutable
Dictionary Data Type
personal_details = { 'name': "Khurram", 'age': 78,
'contact': "03124000464",
'address': "Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan",
}
type(personal_details) dict
personal_details["name"]
'Khurram'
personal_details["address"]
'Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan'
personal_details["postal_code"] = 54600
personal_details
{'name': 'Khurram', 'age': 78,
'contact': '03124000464',
'address': 'Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan', 'postal_code': 54600}
dict Methods
personal_details.items() # Returns a list containing a tuple for each key value pair
dict_items([('name', 'Khurram'), ('age', 78), ('contact', '03124000464'), ('address', 'Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan')])
personal_details.keys() # Returns a list containing the dictionary's keys
dict_keys(['name', 'age', 'contact', 'address'])
personal_details.values() # Returns a list of all the values in the dictionary dict_values(['Khurram', 78, '03124000464', 'Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan'])
Set Data Type
my_set = {1, 2, "khurram", 2, 3}
type(my_set) set
my_set
{1, 2, 3, 'khurram'}
my_set[0]
-
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-166-158c424478a1> in <module>
----> 1 my_set[0]
TypeError: 'set' object is not subscriptable
Note:-
we can not retieve values from a set directly, for this we have to do type casting then retrieve values from set
Type Casting:-
type casting means converting one data type to another data type let say conterting set dtype to list dtype
set_to_list = list(my_set)
set_to_list
['khurram', 1, 2, 3]
type(set_to_list) list
Set Methods
A = {1,2,3}
A.add("wNeuron") # Adds an element to the set
A
{1, 2, 3, 'wNeuron'}
B = {2, 3, 5, 7}
A_intersection_B = A.intersection(B) # Returns a set, that is the intersection of tw
A_intersection_B
{2, 3}
A.pop() # Removes an element from the set 1
A
{2, 3, 'wNeuron'}
A.remove('wNeuron') # Removes the specified element
A
{2, 3}
FrozenSet Data Type
X = {10,11,12}
f_set = frozenset(X)
f_set
frozenset({10, 11, 12})
f_set.add(13)
-
AttributeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-189-a5fe8fb3ef2b> in <module>
----> 1 f_set.add(13)
AttributeError: 'frozenset' object has no attribute 'add'
Bool and None Data Type
status = True
type(status) bool
is_active = False
type(is_active)
bool
initial = None
type(initial)
NoneType
Assignment-2:-
consider the following paragraph given below
my_para = "i started my journy of life in 1980"
convert the above string into a list and remove the words "my journy of life" from the list and display the result
# solution
my_para = "i started my journy of life in 1980"
working_lst = my_para.split(" ")
working_lst
['i', 'started', 'my', 'journy', 'of', 'life', 'in', '1980']
working_lst.remove("my")
working_lst.remove("journy")
working_lst.remove("of")
working_lst.remove("life")
working_lst
['i', 'started', 'in', '1980']
working_lst[0] + " " + working_lst[1] + " " + working_lst[2]+ " " + working_lst[3]
'i started in 1980'
Assignment-3:-
consider the following list given below
my_list = ["red", "blue", "orange", "red", "red", "blue"]
remove the repeated color names from the list of colors so each color apears unique or one time
# solution
my_list = ["red", "blue", "orange", "red", "red", "blue"] my_set = set(my_list)
new_unique_list = list(my_set)
new_unique_list
['orange', 'blue', 'red']
Assignment-4:-
consider the following list given below
my_list = ["red", "blue", "orange"]
add the following items in the above list "Green" and "yellow"
# solution
my_list = ["red", "blue", "orange"] my_list.append("Green") my_list.append("Yellow")
my_list
['red', 'blue', 'orange', 'Green', 'Yellow']
Assignment-5:-
consider the following dict given below
my_dict = {"name": "Ali", "age": 13}
add the following key : cell_no and value : 03124000464 in the above dict
# solution
my_dict = {"name": "Ali", "age": 13} my_dict["cell_no"]= "03124000464" my_dict
{'name': 'Ali', 'age': 13, 'cell_no': '03124000464'}
Assignment-6:-
create a list of dictioneries named profiles, each dictionary has the following attributes
Keys: values
name_of_user: str age: float no_of_brothers: int
names_of_brothers: list cell_numbers: set
experience: list of dicts
experience is also a list of dicts, each dict must have the following keys and values
Keys: values
company_name: str join_date: str
end_date: str
no_of_years_worked: float
Double-click (or enter) to edit
# solution
Print Function/Method
print("my name is khurram") my name is khurram
a = 12
print(a)
12
age = 12
print("age of Ali is :", age) age of Ali is : 12
print("a"*5)
aaaaa
Input function/method
name = input("Enter your name: ") print("your name is :", name)
Enter your name: Khurram your name is : Khurram
